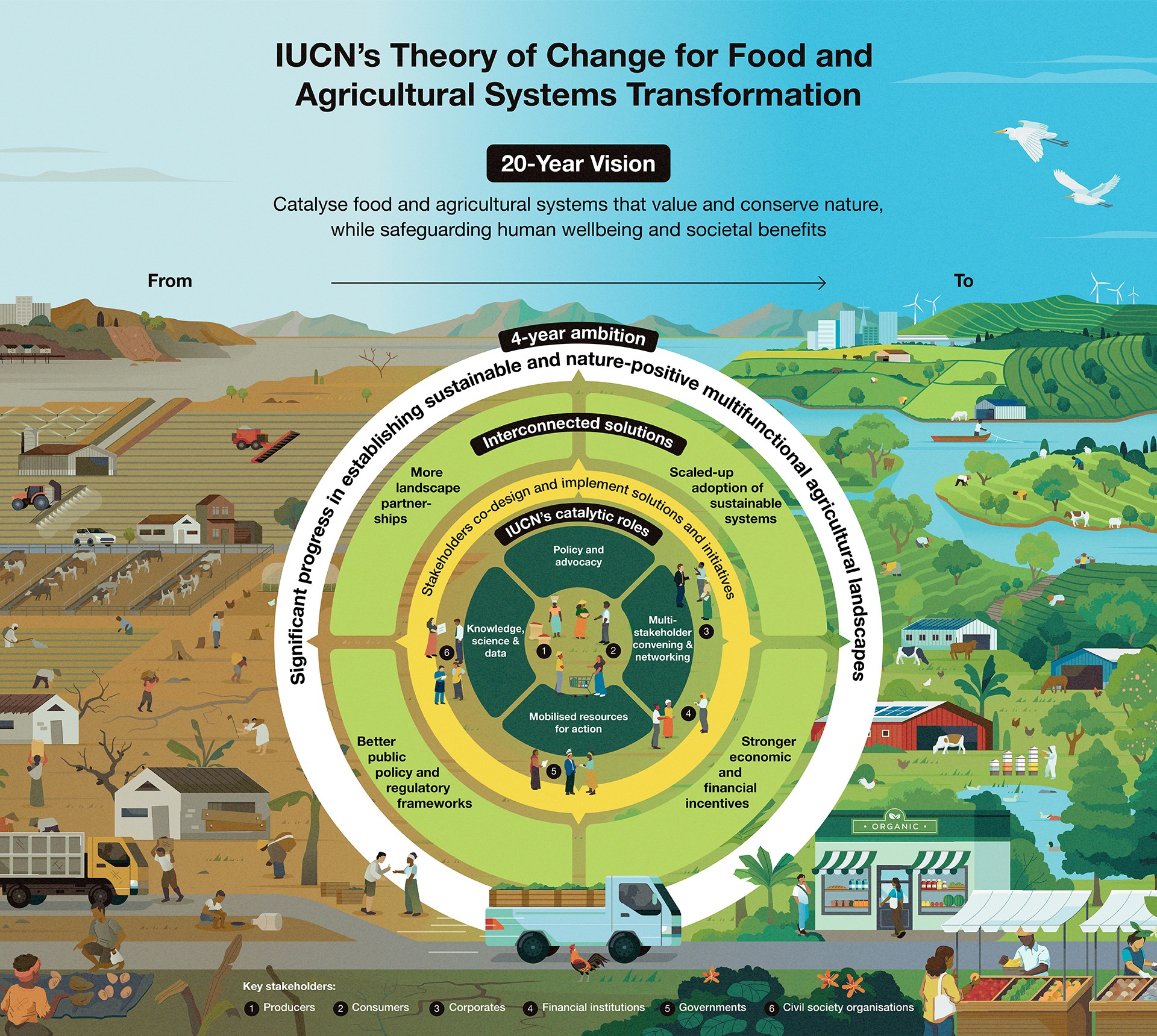
IUCN uses the power of these catalytic roles to achieve the following output (yellow circle):
Conservation and food and agricultural systems actors have co-designed and implemented solutions and initiatives contributing to sustainable and nature-positive multifunctional agricultural landscapes.
The catalytic roles are our levers for transformational change through solutions and initiatives in 4 interconnected solution areas at the next level (light green) of the circle of change:
Better public policy and regulatory frameworks for sustainable food and agricultural systems; we promote reliable scientific information, tools, metrics and monitoring frameworks to governments, improving capacity for evidence-based policymaking and improving policy coherence. We coordinate and train producer organisations and Indigenous Peoples and Local Communities to advocate more powerfully for what they need. By convening participatory and inclusive multistakeholder dialogues we increase trust and consensus between government, producers, corporates, financial institutions, indigenous peoples, conservation and other civil society organizations. As a result, governments at all scales and in all regions adopt coordinated policies and better align financial flows to enable and incentivise sustainable food and agricultural systems, including the increased adoption of sustainable agricultural production systems.
Stronger economic and financial incentives for sustainable food and agricultural systems; we increase awareness and knowledge, strengthening the capacity of financial institutions and agrifood corporates to make policy and investment decisions favouring sustainability. As these investments come on stream, producers gain direct access to finance and markets under better contract terms which encourage them to transition. Alongside this, increased consumer awareness shifts the market and leads to greater demand for sustainably produced food.
Scaled-up adoption of sustainable agricultural production systems by producers including Indigenous peoples and local communities (IPLCs); we promote the integration of local and indigenous knowledge with science and innovation, and strengthen learning and extension systems to catalyse producers’ behaviour change towards the adoption of Nature-based Solutions such as regenerative agriculture, agroecology and organic agriculture. Encouraged by more supportive policies and better economic and financial incentives from consumers, financiers and corporates, producers adopt sustainable agricultural systems at scale.
- More landscape partnerships supporting sustainable food and agricultural systems; we provide access and support to these partnerships to increase their capacity to work on landscape governance, planning and management, and to sustain their action through achieving financial and institutional sustainability.
The multiplier effect between these 4 interconnected solution areas reinforces change and makes the world we want to see more likely to emerge as the “new normal”. In our 4 year ambition (white), we achieve significant progress in establishing sustainable and nature-positive multifunctional agricultural landscapes. This contributes to IUCN’s 20 Year vision: food and agricultural systems that value and conserve nature, while safeguarding human wellbeing and societal benefits.